Customer Stories
How 1NCE scaled global IoT billing with Lago
Finn Lobsien • 2 min read
Jul 3, 2025
/4 min read

Revenue recognition, governed by the ASC 606 and IFRS 15 standards, is the accounting principle that dictates precisely when and how a business can record revenue. For a SaaS company with a tiered plan charging $5,000 per month for its premium tier, revenue is recognized as $5,000 for each month the service is delivered, not as a lump sum of $60,000 when a customer prepays for an annual contract. This accrual-based method is fundamental for accurate financial reporting and providing a true measure of a company's performance.
Adhering to these standards is not merely a compliance exercise; it directly impacts investor confidence, company valuation, and strategic decision-making. A clear revenue recognition policy ensures that financial statements are comparable across different companies and industries, providing a standardized view of performance.
The revenue recognition principle is a core component of accrual accounting. It mandates that revenue is recorded when it is earned and realized, regardless of when the cash payment is received.
For SaaS and subscription businesses, this distinction is critical. An annual software subscription paid upfront is not fully "earned" on day one. The revenue is earned incrementally over the 12-month contract term as the service is provided. This prevents the misrepresentation of a company's financial health and ensures revenue is matched to the period in which it was actually earned.
The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) jointly issued ASC 606 to create a unified framework for revenue recognition from customer contracts. This standard replaces industry-specific guidance with a single, industry-neutral five-step model, enhancing transparency and comparability.
The five steps are:
The choice of a SaaS pricing model directly influences the application of the five-step revenue recognition framework. While simple models present straightforward accounting, complex, usage-based models require a robust billing and revenue recognition infrastructure.
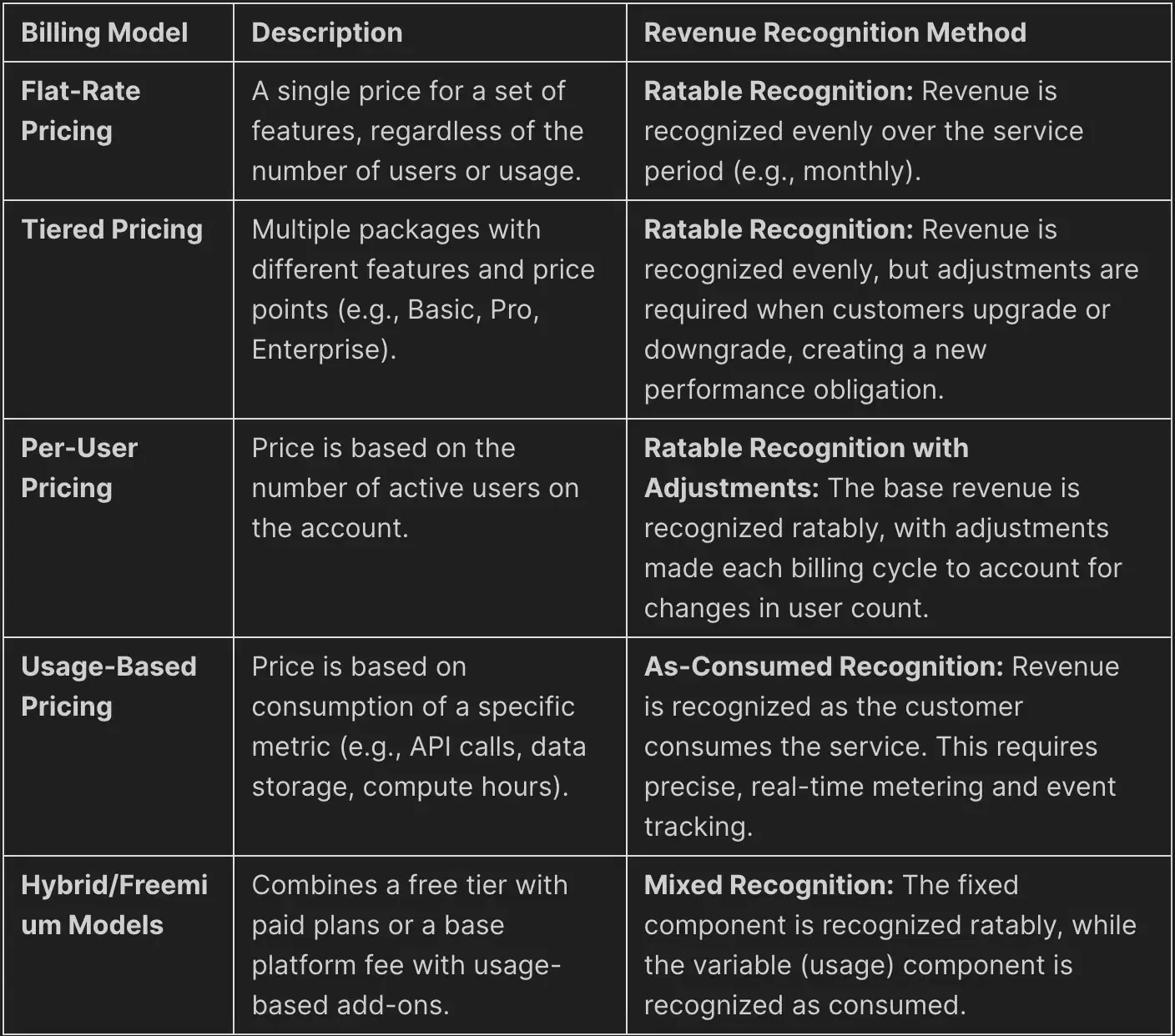
Usage-based and hybrid models, while effective for aligning price with value and boosting Net Revenue Retention (NRR), introduce significant revenue recognition complexity. Manually tracking consumption and allocating revenue in spreadsheets is not scalable and is highly susceptible to errors, posing a serious compliance risk.
To manage the complexities of modern SaaS billing, businesses require an automated system that can handle intricate pricing logic while ensuring ASC 606 compliance. A sophisticated, API-driven billing platform is architected to solve this challenge. By connecting directly to your product's event stream, such a platform can meter any type of usage, apply complex pricing rules, and generate invoices automatically.
This automation extends directly to revenue recognition. The platform tracks the fulfillment of performance obligations—whether over time for a subscription or as-consumed for usage-based charges—and generates the data needed for accurate revenue schedules. This capability dramatically reduces manual effort, minimizes the risk of billing errors, and accelerates the time-to-cash cycle. By providing a compliant, auditable record of revenue, a cloud-native platform ensures that financial reporting is always accurate and up-to-date. For organizations with specific data sovereignty needs, a self-hosted option provides an alternative with the same powerful capabilities.
Why is revenue recognition important for SaaS companies? Accurate revenue recognition is critical for SaaS companies to maintain compliance with GAAP and IFRS standards. It provides a true and fair view of financial performance, which is essential for securing investor funding, calculating company valuation, and making informed strategic decisions. It prevents companies from misstating their financial health by recognizing long-term contract value upfront.
What is the difference between billing and revenue recognition? Billing is the operational process of generating and sending invoices to customers and collecting payment. It is focused on cash flow. Revenue recognition is the accounting process of recording revenue in the financial statements according to accounting standards like ASC 606. For example, you might bill a customer $12,000 on January 1st for an annual subscription, but you will recognize only $1,000 of revenue each month for the next 12 months.
How does ASC 606 specifically affect SaaS businesses? ASC 606 requires SaaS businesses to deconstruct their contracts into distinct performance obligations (e.g., subscription access, setup fees, support) and recognize revenue as each is fulfilled. This is particularly impactful for businesses with hybrid models, as it mandates separating recurring subscription revenue (recognized over time) from one-time fees or usage-based charges (recognized when delivered or as consumed).